Introduction
Overview
Teaching: 5 min
Exercises: 5 minQuestions
What are containers?
Objectives
First learning objective.
Documentation
The official Docker documentation and tutorial can be found on the Docker website. It is quite thorough and useful. It is an excellent guide that should be routinely visited, but the emphasis of this introduction is on using Docker, not how Docker itself works.
A note up front, Docker has very similar syntax to Git and Linux, so if you are familiar with the command line tools for them then most of Docker should seem somewhat natural (though you should still read the docs!).
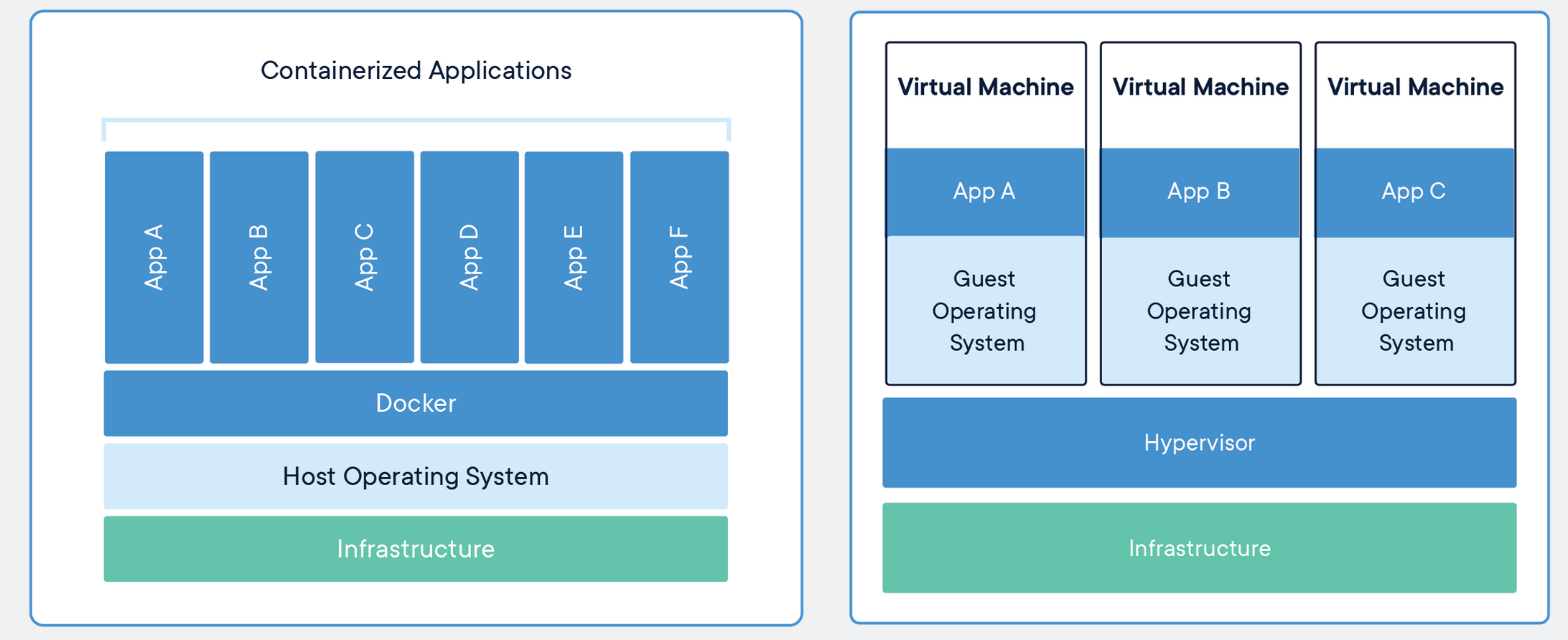
Docker Images and Containers
It is still important to know what Docker is and what the components of it are. Docker images are executables that bundle together all necessary components for an application or an environment. Docker containers are the runtime instances of images — they are images with a state.
Importantly, containers share the host machine’s OS system kernel and so don’t require an OS per application. As discrete processes containers take up only as much memory as necessary, making them very lightweight and fast to spin up to run.
Singularity
Docker is the most popular containerization tool these days, particularly in industry, but it’s not the only one. There are other kids on the block including Rocket and Singularity which are in use, but just haven’t gained as much large-scale traction.
Singularity in particular is used widely in HPC, and particularly by CMS, so you may have need to familiarize yourself with it at some point.
The RECAST FAQ includes a brief intro to the important differences between docker and singularity.
Key Points
First key point. Brief Answer to questions.
