HiggsToTauTau analysis: parallel
Overview
Teaching: 10 min
Exercises: 20 minQuestions
Challenge: write the HiggsToTauTau analysis parallel workflow and run it on REANA
Objectives
Develop a full HigssToTauTau analysis workflow using parallel language
Overview
We have seen an example of a full DAG-aware workflow language called Yadage and how it can be used to describe and run the RooFit example and a simple version of HiggsToTauTau example.
In this episode we shall see how to efficiently apply parallelism to speed up the HiggsToTauTau example via the scatter-gather paradigm introduced in the previous episode.
HiggsToTauTau analysis
The overall reana.yaml looks like:
version: 0.6.0
inputs:
parameters:
files:
- root://eospublic.cern.ch//eos/root-eos/HiggsTauTauReduced/GluGluToHToTauTau.root
- root://eospublic.cern.ch//eos/root-eos/HiggsTauTauReduced/VBF_HToTauTau.root
- root://eospublic.cern.ch//eos/root-eos/HiggsTauTauReduced/DYJetsToLL.root
- root://eospublic.cern.ch//eos/root-eos/HiggsTauTauReduced/TTbar.root
- root://eospublic.cern.ch//eos/root-eos/HiggsTauTauReduced/W1JetsToLNu.root
- root://eospublic.cern.ch//eos/root-eos/HiggsTauTauReduced/W2JetsToLNu.root
- root://eospublic.cern.ch//eos/root-eos/HiggsTauTauReduced/W3JetsToLNu.root
- root://eospublic.cern.ch//eos/root-eos/HiggsTauTauReduced/Run2012B_TauPlusX.root
- root://eospublic.cern.ch//eos/root-eos/HiggsTauTauReduced/Run2012C_TauPlusX.root
cross_sections:
- 19.6
- 1.55
- 3503.7
- 225.2
- 6381.2
- 2039.8
- 612.5
- 1.0
- 1.0
short_hands:
- [ggH]
- [qqH]
- [ZLL,ZTT]
- [TT]
- [W1J]
- [W2J]
- [W3J]
- [dataRunB]
- [dataRunC]
workflow:
type: yadage
file: workflow.yaml
outputs:
files:
- fit/fit.png
Note that we define input files and cross sections and short names as an array. It is this array that we shall be scattering around.
HiggsToTauTau skimming
The skimming step definition looks like:
- name: skim
dependencies: [init]
scheduler:
scheduler_type: multistep-stage
parameters:
input_file: {step: init, output: files}
cross_section: {step: init, output: cross_sections}
output_file: '{workdir}/skimmed.root'
scatter:
method: zip
parameters: [input_file, cross_section]
step: {$ref: 'steps.yaml#/skim'}
where the step is defined as:
skim:
process:
process_type: 'interpolated-script-cmd'
script: |
./skim {input_file} {output_file} {cross_section} 11467.0 0.1
environment:
environment_type: 'docker-encapsulated'
image: gitlab-registry.cern.ch/awesome-workshop/awesome-analysis-eventselection-stage3
imagetag: master
publisher:
publisher_type: interpolated-pub
publish:
skimmed_file: '{output_file}'
Note the scatter paradigm that will cause nine parallel jobs for each input dataset file.
HiggsToTauTau histogramming
The histograms can be produced as follows:
- name: histogram
dependencies: [skim]
scheduler:
scheduler_type: multistep-stage
parameters:
input_file: {stages: skim, output: skimmed_file}
output_names: {step: init, output: short_hands}
output_dir: '{workdir}'
scatter:
method: zip
parameters: [input_file, output_names]
step: {$ref: 'steps.yaml#/histogram'}
with:
histogram:
process:
process_type: 'interpolated-script-cmd'
script: |
for x in {output_names}; do
python histograms.py {input_file} $x {output_dir}/$x.root;
done
environment:
environment_type: 'docker-encapsulated'
image: gitlab-registry.cern.ch/awesome-workshop/awesome-analysis-eventselection-stage3
imagetag: master
publisher:
publisher_type: interpolated-pub
glob: true
publish:
histogram_file: '{output_dir}/*.root'
HiggsToTauTau merging
Gather time! How do we merge scattered results?
- name: merge
dependencies: [histogram]
scheduler:
scheduler_type: singlestep-stage
parameters:
input_files: {stages: histogram, output: histogram_file, flatten: true}
output_file: '{workdir}/merged.root'
step: {$ref: 'steps.yaml#/merge'}
with:
merge:
process:
process_type: 'interpolated-script-cmd'
script: |
hadd {output_file} {input_files}
environment:
environment_type: 'docker-encapsulated'
image: gitlab-registry.cern.ch/awesome-workshop/awesome-analysis-eventselection-stage3
imagetag: master
publisher:
publisher_type: interpolated-pub
publish:
merged_file: '{output_file}'
HiggsToTauTau fitting
The fit can be performed as follows:
- name: fit
dependencies: [merge]
scheduler:
scheduler_type: singlestep-stage
parameters:
histogram_file: {step: merge, output: merged_file}
fit_outputs: '{workdir}'
step: {$ref: 'steps.yaml#/fit'}
with:
fit:
process:
process_type: 'interpolated-script-cmd'
script: |
python fit.py {histogram_file} {fit_outputs}
environment:
environment_type: 'docker-encapsulated'
image: gitlab-registry.cern.ch/awesome-workshop/awesome-analysis-statistics-stage3
imagetag: master
publisher:
publisher_type: interpolated-pub
publish:
fit_results: '{fit_outputs}/fit.png'
HiggsToTauTau plotting
Challenge time! Add plotting step to the workflow.
Exercise
Following the example above, write plotting step and plug it into the overall workflow.
Solution
- name: plot dependencies: [merge] scheduler: scheduler_type: singlestep-stage parameters: histogram_file: {step: merge, output: merged_file} plot_outputs: '{workdir}' step: {$ref: 'steps.yaml#/plot'}with:
plot: process: process_type: 'interpolated-script-cmd' script: | python plot.py {histogram_file} {plot_outputs} 0.1 environment: environment_type: 'docker-encapsulated' image: gitlab-registry.cern.ch/awesome-workshop/awesome-analysis-eventselection-stage3 imagetag: master publisher: publisher_type: interpolated-pub publish: fitting_plot: '{plot_outputs}'
Full workflow
Assembling the previous stages visually, the full workflow looks like:
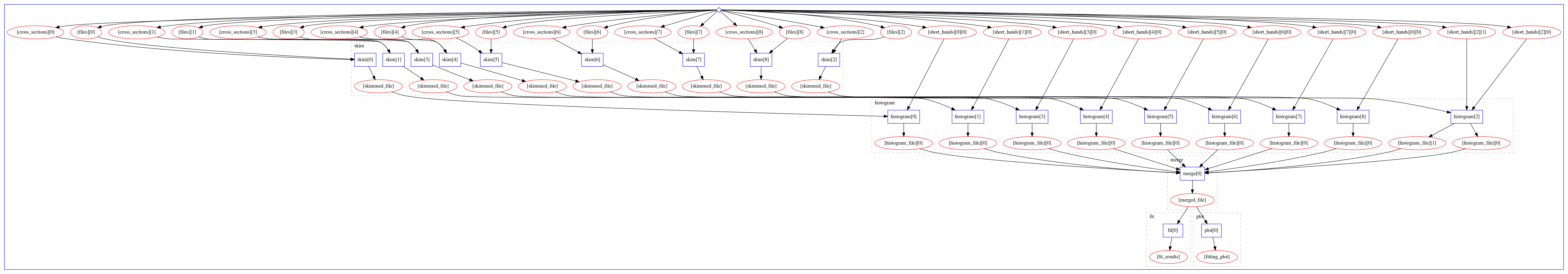
Running full workflow
We are now ready to run the example of REANA cloud.
Exercise
Run HiggsToTauTau parallel workflow on REANA cloud. How many job does the workflow have? How much faster it is executed when compared to the simple Serial version?
Solution
reana.yaml:
version: 0.6.0 inputs: parameters: files: - root://eospublic.cern.ch//eos/root-eos/HiggsTauTauReduced/GluGluToHToTauTau.root - root://eospublic.cern.ch//eos/root-eos/HiggsTauTauReduced/VBF_HToTauTau.root - root://eospublic.cern.ch//eos/root-eos/HiggsTauTauReduced/DYJetsToLL.root - root://eospublic.cern.ch//eos/root-eos/HiggsTauTauReduced/TTbar.root - root://eospublic.cern.ch//eos/root-eos/HiggsTauTauReduced/W1JetsToLNu.root - root://eospublic.cern.ch//eos/root-eos/HiggsTauTauReduced/W2JetsToLNu.root - root://eospublic.cern.ch//eos/root-eos/HiggsTauTauReduced/W3JetsToLNu.root - root://eospublic.cern.ch//eos/root-eos/HiggsTauTauReduced/Run2012B_TauPlusX.root - root://eospublic.cern.ch//eos/root-eos/HiggsTauTauReduced/Run2012C_TauPlusX.root cross_sections: - 19.6 - 1.55 - 3503.7 - 225.2 - 6381.2 - 2039.8 - 612.5 - 1.0 - 1.0 short_hands: - [ggH] - [qqH] - [ZLL,ZTT] - [TT] - [W1J] - [W2J] - [W3J] - [dataRunB] - [dataRunC] workflow: type: yadage file: workflow.yaml outputs: files: - fit/fit.pngworkflow.yaml:
stages: - name: skim dependencies: [init] scheduler: scheduler_type: multistep-stage parameters: input_file: {step: init, output: files} cross_section: {step: init, output: cross_sections} output_file: '{workdir}/skimmed.root' scatter: method: zip parameters: [input_file, cross_section] step: {$ref: 'steps.yaml#/skim'} - name: histogram dependencies: [skim] scheduler: scheduler_type: multistep-stage parameters: input_file: {stages: skim, output: skimmed_file} output_names: {step: init, output: short_hands} output_dir: '{workdir}' scatter: method: zip parameters: [input_file, output_names] step: {$ref: 'steps.yaml#/histogram'} - name: merge dependencies: [histogram] scheduler: scheduler_type: singlestep-stage parameters: input_files: {stages: histogram, output: histogram_file, flatten: true} output_file: '{workdir}/merged.root' step: {$ref: 'steps.yaml#/merge'} - name: fit dependencies: [merge] scheduler: scheduler_type: singlestep-stage parameters: histogram_file: {step: merge, output: merged_file} fit_outputs: '{workdir}' step: {$ref: 'steps.yaml#/fit'} - name: plot dependencies: [merge] scheduler: scheduler_type: singlestep-stage parameters: histogram_file: {step: merge, output: merged_file} plot_outputs: '{workdir}' step: {$ref: 'steps.yaml#/plot'}steps.yaml:
skim: process: process_type: 'interpolated-script-cmd' script: | ./skim {input_file} {output_file} {cross_section} 11467.0 0.1 environment: environment_type: 'docker-encapsulated' image: gitlab-registry.cern.ch/awesome-workshop/awesome-analysis-eventselection-stage3 imagetag: master publisher: publisher_type: interpolated-pub publish: skimmed_file: '{output_file}' histogram: process: process_type: 'interpolated-script-cmd' script: | for x in {output_names}; do python histograms.py {input_file} $x {output_dir}/$x.root; done environment: environment_type: 'docker-encapsulated' image: gitlab-registry.cern.ch/awesome-workshop/awesome-analysis-eventselection-stage3 imagetag: master publisher: publisher_type: interpolated-pub glob: true publish: histogram_file: '{output_dir}/*.root' merge: process: process_type: 'interpolated-script-cmd' script: | hadd {output_file} {input_files} environment: environment_type: 'docker-encapsulated' image: gitlab-registry.cern.ch/awesome-workshop/awesome-analysis-eventselection-stage3 imagetag: master publisher: publisher_type: interpolated-pub publish: merged_file: '{output_file}' fit: process: process_type: 'interpolated-script-cmd' script: | python fit.py {histogram_file} {fit_outputs} environment: environment_type: 'docker-encapsulated' image: gitlab-registry.cern.ch/awesome-workshop/awesome-analysis-statistics-stage3 imagetag: master publisher: publisher_type: interpolated-pub publish: fit_results: '{fit_outputs}/fit.png' plot: process: process_type: 'interpolated-script-cmd' script: | python plot.py {histogram_file} {plot_outputs} 0.1 environment: environment_type: 'docker-encapsulated' image: gitlab-registry.cern.ch/awesome-workshop/awesome-analysis-eventselection-stage3 imagetag: master publisher: publisher_type: interpolated-pub publish: fitting_plot: '{plot_outputs}'
Key Points
Use step dependencies to express main analysis stages
Use scatter-gather paradigm in staged to massively parallelise DAG workflow execution
REANA usage scenarios remain the same regardless of workflow language details